Windows PE
Windows Architecture
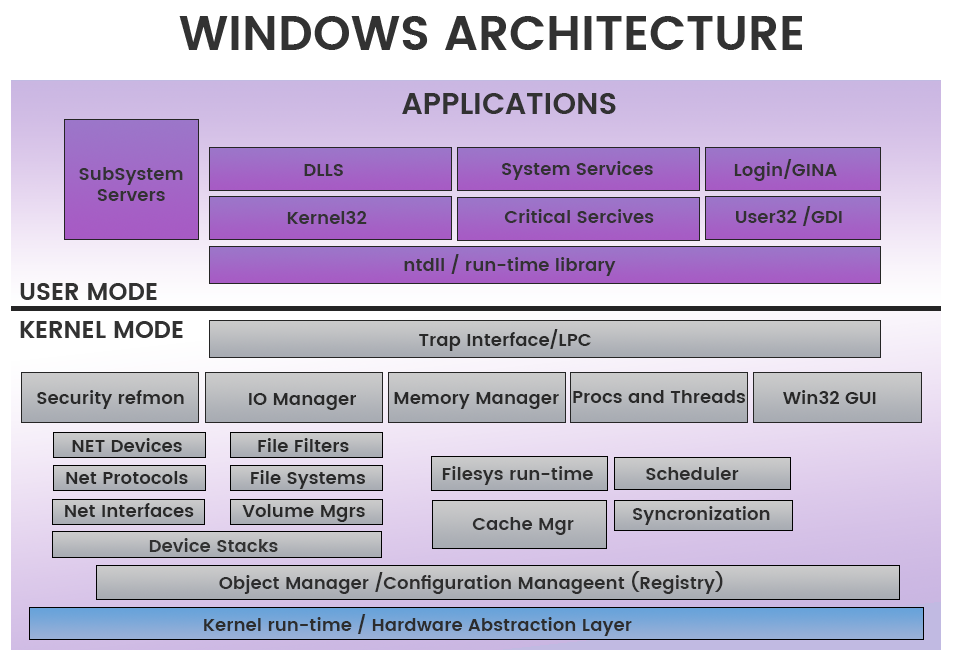
User-mode vs. Kernel Mode [1]
In user-mode, an application starts a user-mode process which comes with its own private virtual address space and handle table
In kernel mode, applications share virtual address space.
This diagram shows the relationship of application components for user-mode and kernel-mode.
PE Header
The PE header provides information to operating system on how to map the file into memory. The executable code has designated regions that require a different memory protection (RWX)
Read
Write
Execute
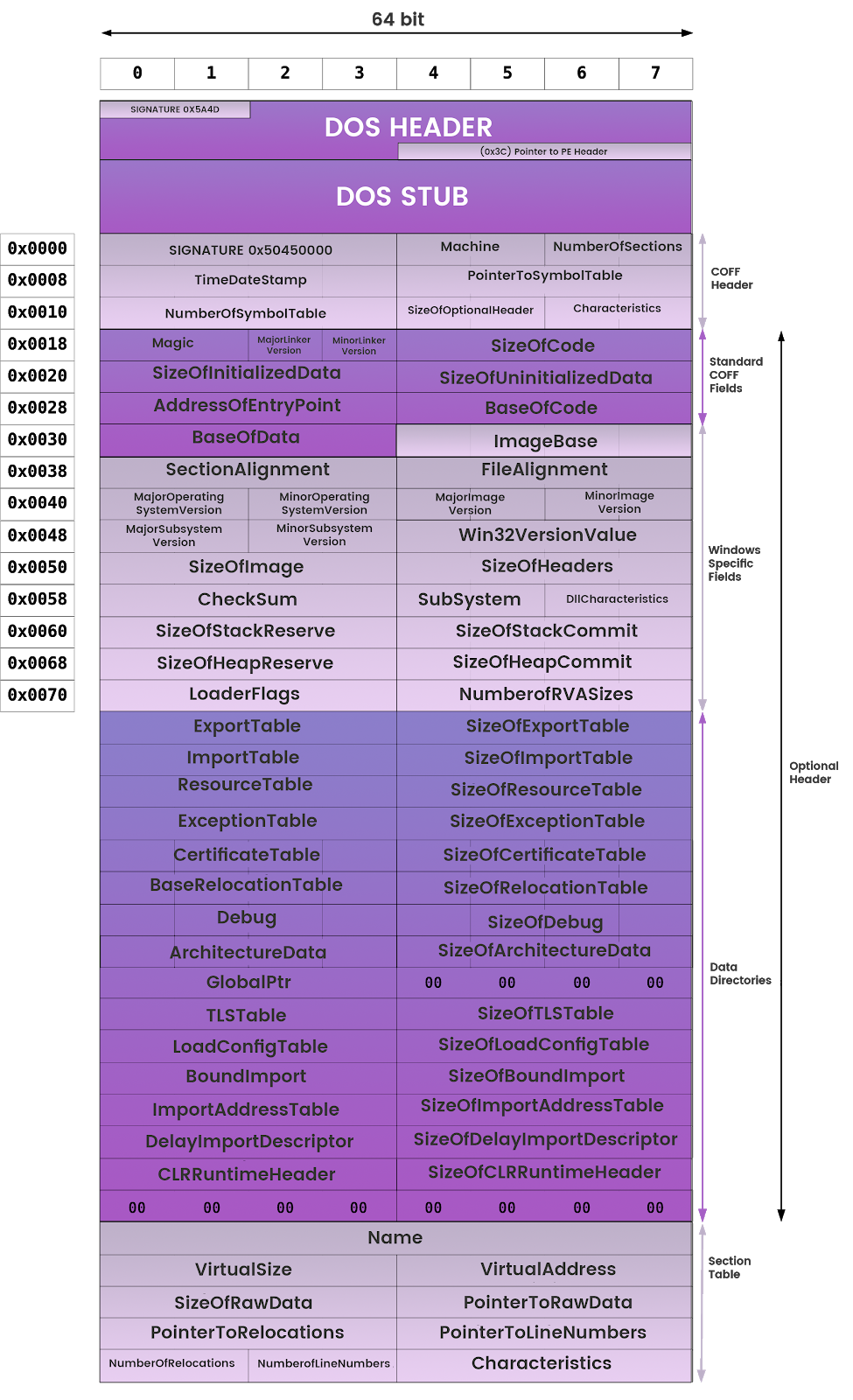
Here is a hexcode dump of a PE header we will be working with.
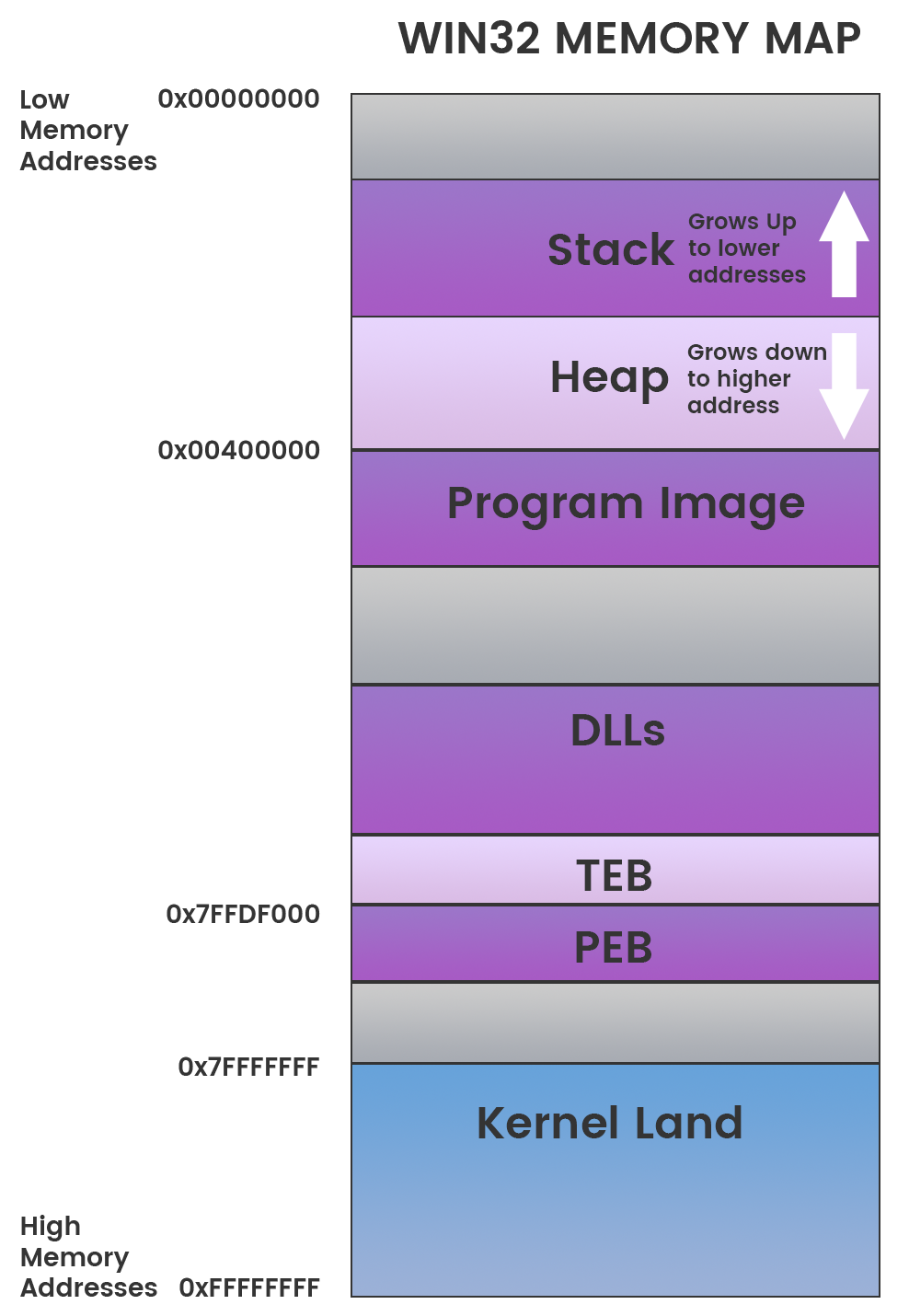
Memory Layout
Stack - region of memory is added or removed using "last-in-first-out" (LIFO) procedure[2]
Heap - region for dynamic memory allocation[3]
Program Image - The PE executable code placed into memory
DLLs - Loaded DLL images that are referenced by the PE
TEB - Thread Environment Block stores information about the current running thread(s)[4]
PEB - Process Environment Block stores information about loaded modules and processes.[5]
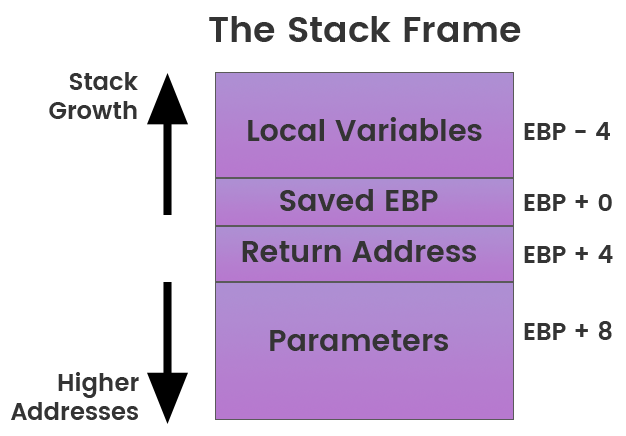
The Stack
Data is either pushed onto or popped off of the stack data structure
EBP - Base Pointer is the register that used to store the references in the stack frame
Last updated